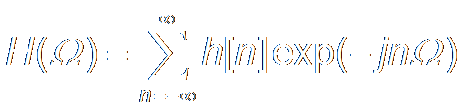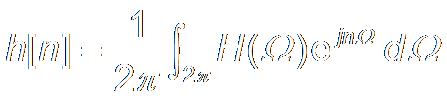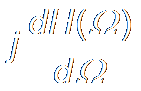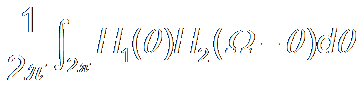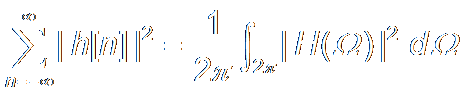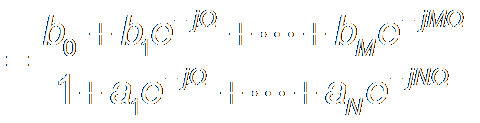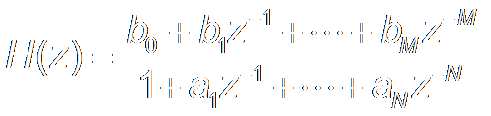|
||
|
|
|
Diff. Eq., Transfer Function & DTFT
Homework: p274: 7.1, p275: 7.5, p278: 7.20
Frequency Response频率响应 The discrete time Fourier transform (DTFT) of System Impulse Response.
Properties Given H(Ω) of h[n]: P1. Periodicity H(Ω) = H(Ω+2π) P2. Time Delay F{ h[n-M] } = exp(-jMΩ) H (Ω) P3. Frequency Shift # F{ exp(-jΩ0n) h[n] } = H (Ω + Ω0) P4. Linearity F{ a h1[n] + b h2[n] } = aH1 (Ω) + b H2 (Ω) where H1(Ω)=F{h1[n] }, H2(Ω)=F{ h2[n] } P5. Conjugacy # F{ h* [n] } = H* (-Ω) When h[n] is real, H* (-Ω) = H (Ω)
P6. Difference F{ h[n] - h[n-1] } = [1-exp(-jΩ)] H (Ω)
P7. Flipping # F{ h[-n] } = H (-Ω)
P8. Upsampling # F{ h[n/k] } = H (kΩ)
P9. Differential #
P10. Convolution # F{ x[n] * h[n] } = X(Ω) H(Ω) where F{ h[n] } = H(Ω) , F{ x[n] } = X(Ω)
P11. Product #
where F{ h1[n] } = H1(Ω) , F{ h2[n] } = H2(Ω)
P12. Parseval Theorem: #
|H (Ω)|2 : Power Spectrum Density
Difference Equation, Transfer Function & DTFT
Difference Equation of ARMA Model 自回归滑动平均模型的差分方程 a0y[n] + a1y[n-1] + L + aNy[n-N] = b0x[n] + b1x[n-1] + L + bMx[n-M] After DTFT using P2, Y(Ω) [a0 + a1e-jΩ + L + aNe-jNΩ ] = X(Ω) [b0 + b1e-jΩ + L + bMe-jMΩ ] So, H(Ω) = Y(Ω) / X(Ω)
Transfer Function
z => exp(jΩ)
Sinusoid Explanation When the input x[n] is sinusoidal, x[n] = A cos(nΩ0 +Φx) Short form notation of DTFT X(Ω0) = A Ð Φx , H(Ω0) = G Ð Φ According to Y(Ω) = X(Ω)H(Ω) We have Y(Ω0) = X(Ω0)H(Ω0) = AG Ð (Φx+Φ) Thus y[n] = AG cos(nΩ0 +Φx+Φ) Frequency Response is a collection Magnitude Gain & Phase Delay for all the frequencies. H(Ω) = G(Ω) Ð Φ(Ω)
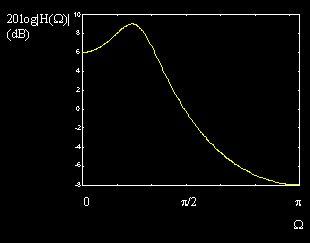
Magnitude & Phase Response The Shape of the filter is the shape of the Magnitude Response. Rewrite H(Ω) into: H(Ω) = |H(Ω)| Ð Φ(Ω) H(Ω + 2π) = H(Ω) |H(-Ω)| = |H(Ω)| Φ(-Ω) = - Φ(Ω)
Magnitude Response Phase Response
Filter Response
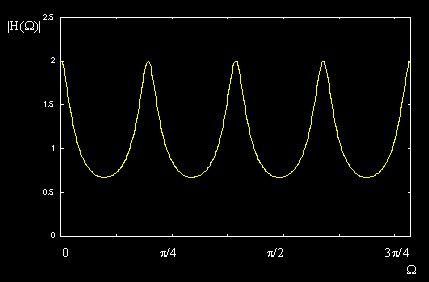
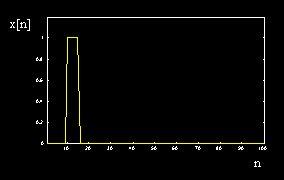
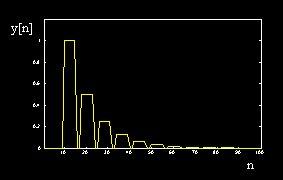
Filters Examples: Comb Filter 梳状滤波器 Comb Filter Input Comb Filter Output
Input (“Hello? Output (“Hello hello?
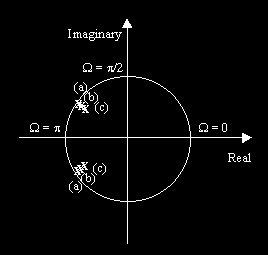
Poles, Zeros & Filter’s Shape Single Pole Filter:
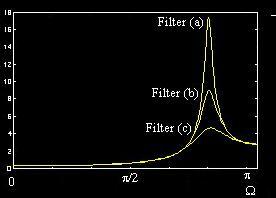
Three 2-Pole Filters
Any Filter:
Page 267, Example 7.24 25 26
|
|
|