|
Region Of
Convergence (ROC)
收敛域
System
Stability系统稳定性
Homework:
p225: 6.28, p229: 6.35
Region of Convergence (ROC)
收敛域
|
x[n]
|
d [n]
|
u [n]
|
b n u[n]
|
n u[n]
|
|
X(z)
|
1
|
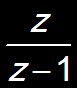
|
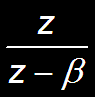
|
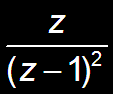
|
|
ROC
|
All z
|
|z|>1
|
|z|>b
|
|z|>1
|
Geometric几何(Power幂级数) Series序列:
Convergence
Condition收敛条件:
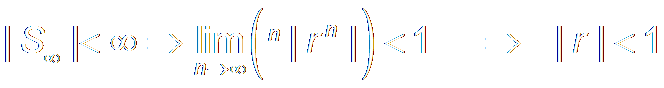
ROC of Finite Sample Series
有限样本序列
z ≠ 0 and/or z
≠ ∞ Q1: Y?
ROC of Right Side Series右边序列
|
Z Transform:
|
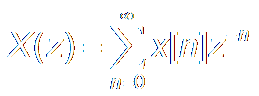
|
|
Convergence
Condition:
|
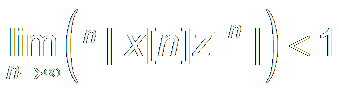
|
ROC of Left Side Series左边序列
|
Z Transform:
|
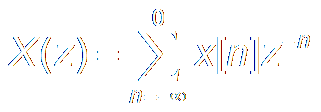
|
|
Convergence
Condition:
|
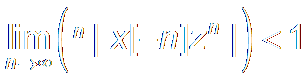
|
ROC of Double Side Series双边序列
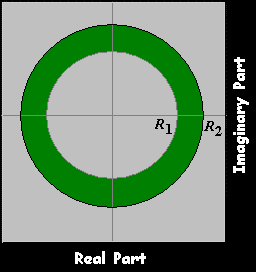
where
R1, R2 must satisfy:
R1<R2
Q:
Deduce推导 the
Z transform of -u[-n-1],
then
find its ROC.
System
Stability系统稳定性
The Poles and
Zeros极点和零点
From Transfer
Function传递函数

Zeros零点 are Roots of
b0zN + b1zN-1
+ b2zN-2 + ··?+ bMzN-M = 0
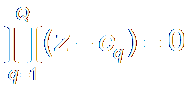
Zeros: {cq ; q=1,2, ··? Q } ,
Q is the highest order of
numerator分子.
Poles极点 are Roots of
a0zN + a1zN-1
+ a2zN-2 + ··?+ aN = 0
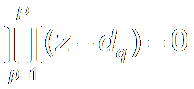
Poles: {dp ; n=1,2,
··? P}
P is the highest order of
denominator分母.
|
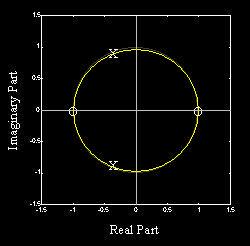
Pole-Zero
Plot
零极点图
"X":
Poles极点
"O": Zeros零点
|
|
Stability稳定性& ROC
For Discrete
Time, Linear Time Invariant (LTI)
system h[n],
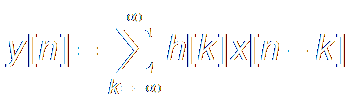
When |x[n]|<B , if |y[n]|<∞,
the system is Stable.
It is equivalent to: The system is Absolutely
Summable. 绝对可和
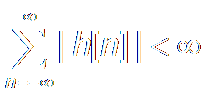
It is the same thing of
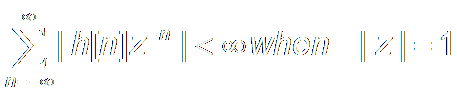
This means: H(z) is Convergent on the unit circle.
Conclusion:
If
a LTI system is stable, the ROC of its
H(z) must include unit circle.
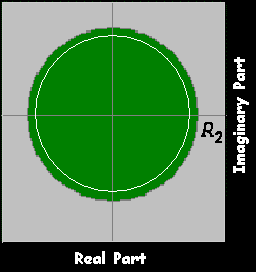 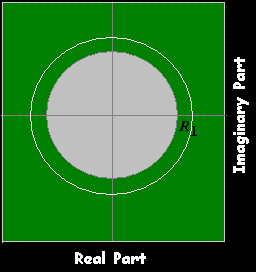 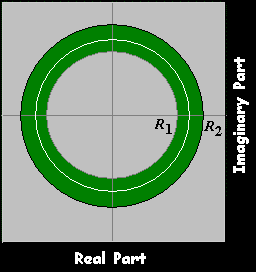
Left
Side
Right
Side
Double Sides
|z|<R2 ,R2≥1
|z|>R1 ,R1≤1
R1<|z|<R2 ,R1≤1≤
R2
Poles to Stability极点与稳定性
If Any Pole lies outside the unit circle,
System is Unstable 不稳定.
If the Outermost最远的
Pole is on the unit circle,
System is
Marginally Stable边缘稳定.
Only when All Poles
are inside the unit circle,
System is Stable稳定.

Stability Region for Poles
极点稳定域
The Partial Fraction
Expansion of X(z):
部分分式展开
If
there is a pole outside unit circle,
that means |βk|>1, then the corresponding
sub-system:
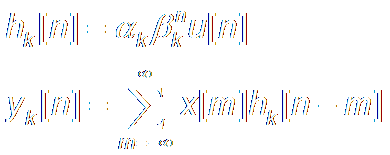
|x[n]|<B , |yk[n]| →∞,
sub-system Not stable,
Thus the whole
system is Unstable.
Responses of Stable System
稳定系统的响应
|
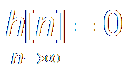
|

|
常数
|
h[n]: Impulse Response; s[n]:
Step Response
冲激响应
阶跃响应
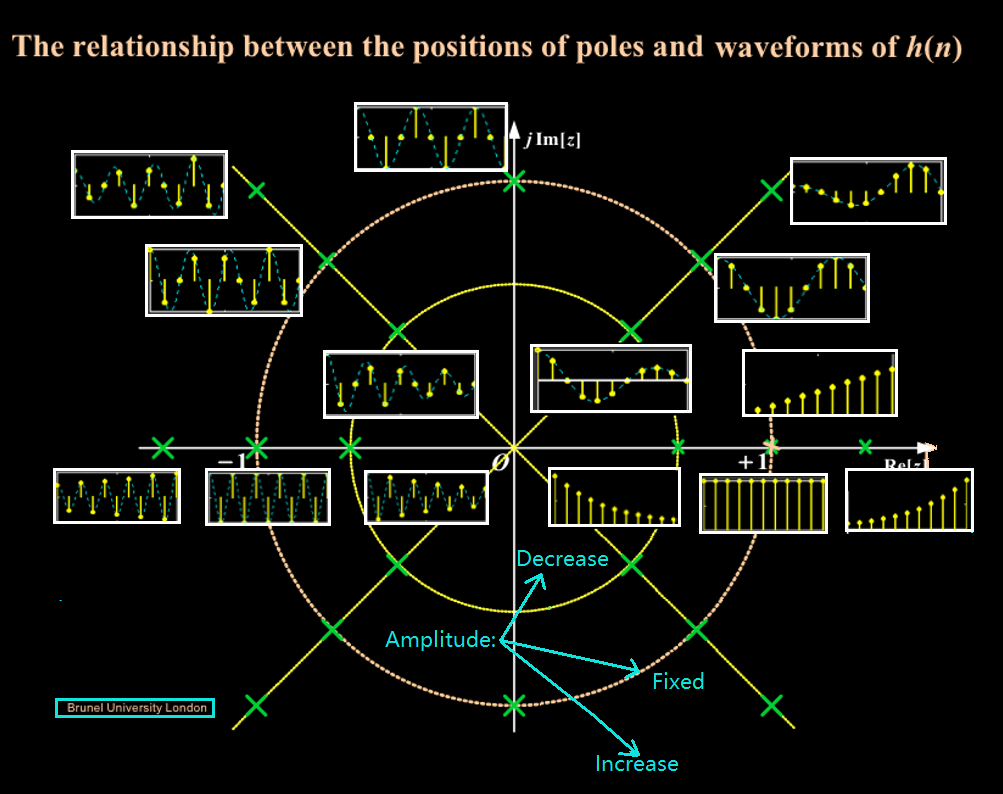
Page 213 Fig6.24; Page 220 Fig6.26.
The Closer the poles are to the origin,
the Faster the system reach its Steady State.
If
poles are on the Left half of Z plane,
the Responses alternate交替 between
Positive and Negative sample by sample.
The
Closer the zeros are to the poles,
the Greater the response being Attenuated衰减.
|