|
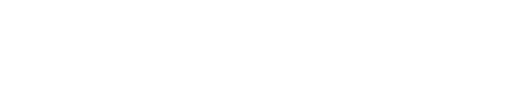

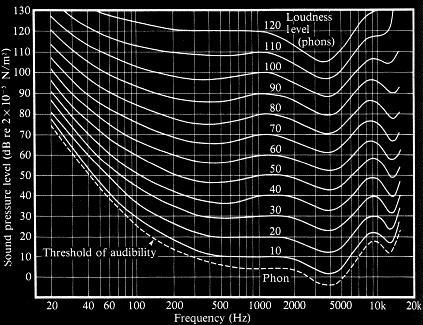
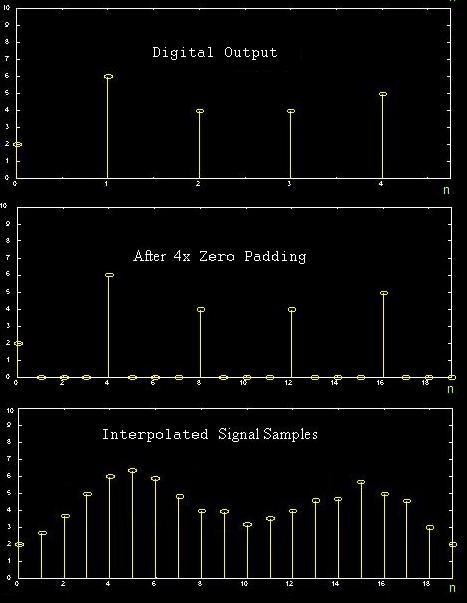
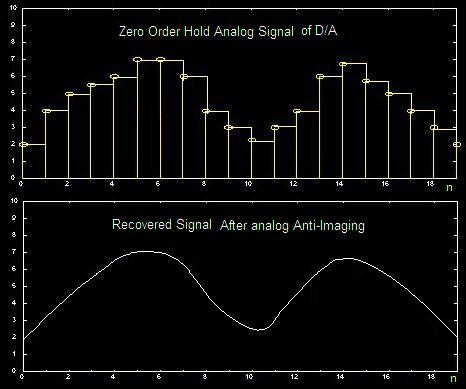
Aliasing
Imaging
混迭
镜像
Spectral Leakage (Smearing)
谱泄漏
拖尾
Finite Word Length Effect
有限字长效应
Aliasing
Frequency Domain
Time Domain
Stereo CD
audio signals:
Sampling Rate: 44100 Hz
16 bits per sample;
Bit Rate: 2x16x44100 = 1.41 Mbps
MP3: Nearly CD Quality, but Bit Rate is only 128 Kbps.
Perceptual Time Decimation:
Weak sounds next to a very loud sound;
Weak sounds below Human Hearing Threshold.
Sound
intensity: The sound power per unit area.

An Audibility Threshold Tester could
be found at:
http://www.phys.unsw.edu.au/~jw/hearing.html
Imaging
Frequency Domain
Time Domain
Spectral Leakage (Smearing)
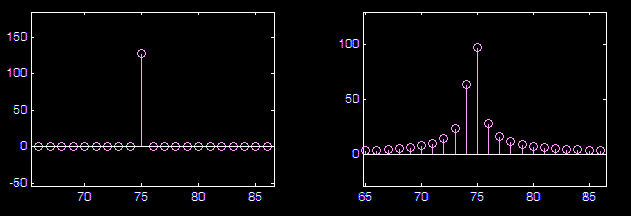
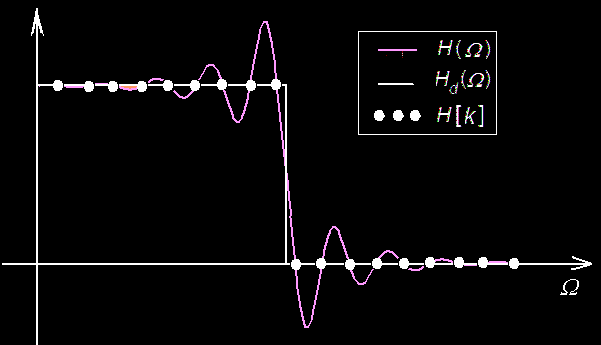
Windowing: Hanning, Hamming, Blackman, Kaiser
Finite Word
Length Effect
Notations
of Decimal(小数)
bN...b3b2b1b0
?/span>b-1b-2b-3...b-M
Natural Decimal System g = 10 , bi = 0,1,2, ...,
9.
Binary System: g = 2 , bi = 0 or 1.
Fixed
Point Number:
b0 ?/span>b1b2b3...bM
(Original Coding)
x = - (2-2
+ 2-3 +2-6 ) = - 0.390625
For any number outside [-1,1]:
y = x 10K
Complementary Code补码 for Negative Number:
|

?[x]c=1?/span> b1b2b3...bM
+ 0?/span>000...
01
|
|
x = -0.3125
[x]o= 1.0101 (-0.3125)
[x]-=
1.1010 (-0.625)
[x]c= 1.1011 (-0.6875)= - (1+x)
Floating
Point Number:
s e1e2e3...eN
b1b2b3...bM
E = e1e2e3...eN
B = 0?/span>b1b2b3...bM
x = (-1)1 21 (2-1 + 2-3
) = -1.25
Standard IEEE 754: Es = E -
2N-1
Single: ?N =8
, ?M =23
Double: N =11 , M =52
Errors of Fixed Point
Number
Truncation
Error
Using L-Bit to present a positive number
that needs M bits, the maximum Truncation Error:
|
For Negative number,
|
|
|
Since Quantization Step is q = 2-L ,
-q < eT ≤
0
Round Error
|x|
= 0?/span>b1b2b3...bLbL+1...bM
|R[x]| =(0?/span>b1b2b3...bLbL+1...bM
+ 0?/span>0 0 0... 0 1)L
So, -q/2 < eR = |R[x]|
- |x| ≤ q/2, q = 2-L
?/span>
Statistical Analysis
of
Quantization Error
Both eT & eR are :
Stationary Random Process;
They are irrelevant to x;
They are white noises;
They obey the Uniform Probability Distribution.
For Fixed Point Number:
μT = -q/2 σ2T = q2/12 μR = 0 σ2R = q2/12
SNR
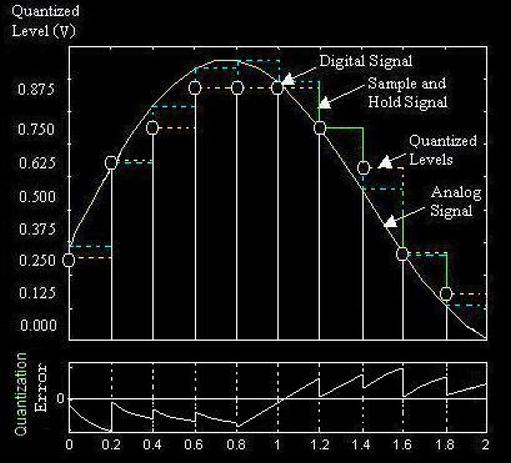
Quantization Error
~ in A/D
~ in
Coefficients
Round: x > [x]R or x < [x]R
|
0.3126
|
0.011 (0.375)
|
|
0.3750
|
|
0.4374
|
~ in Calculations
Overflow溢出
|
x1?/span>(6/8)
|
0.110
|
|
x2 (3/8)
|
0.011
|
|
x1+x2?/span>(9/8)
|
1.001 (-1/8)
|
Truncation截断:
Always x < [x]R
|
x1?/span>(6/8)
|
0.101_
|
|
x2 (3/8)
|
x 0.011_
|
|
x1?/span>* x2?/span>(9/32)
|
101_
101 _
|
|
(1/8) 0.001111_
|
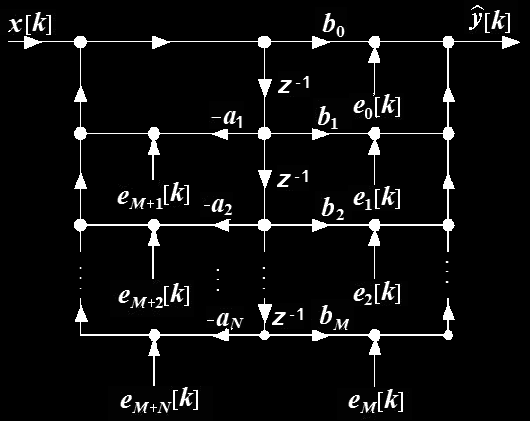
Minimize Finite Word
Length Effect
More bits
Better Filter Structure
y[n]
= b0x[n] + b1x[n-1]
+ L +
bMx[n-M]
- a1y[n-1] - L - aNy[n-N]
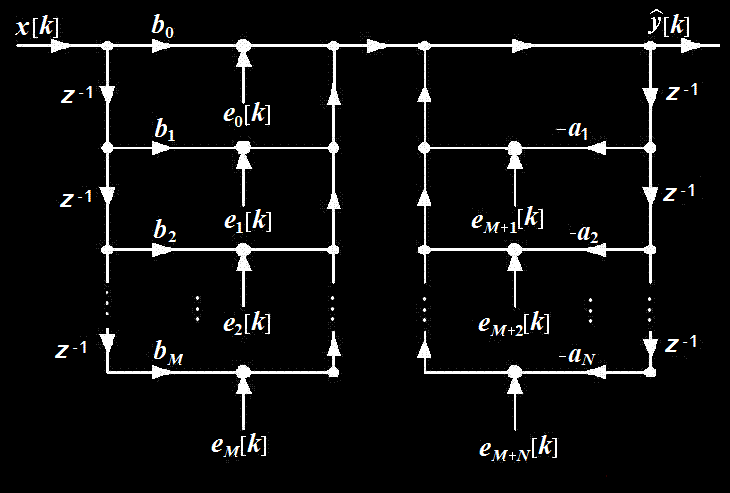
More Storage
Less Storage
Using Second Order System
(SOS)
Page 116 Fig.4.16
|